Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 29 | 30 | 31 |
Tags
- 릿코드 파이썬
- 알고리즘풀기
- 상가수익률계산기
- 릿코드 풀기
- 코틀린기초
- 릿코드
- binary search
- leetcode 풀기
- 파이썬릿코드풀기
- leetcode풀이
- python priority queue
- LeetCode
- python 릿코드
- 파이썬릿코드
- 파이썬 릿코드
- python 알고리즘
- 파이썬 알고리즘 풀기
- 파이썬 프로그래머스
- python Leetcode
- 알고리즘풀이
- 잇츠디모
- leetcode풀기
- python xor
- 파이썬알고리즘풀기
- 릿코드풀이
- python sorted
- 파이썬알고리즘
- 릿코드풀기
- python zip_longest
- 파이썬 알고리즘
Archives
- Today
- Total
소프트웨어에 대한 모든 것
LeetCode 풀기 - 21. Merge Two Sorted Lists 본문
반응형
21. Merge Two Sorted Lists
https://leetcode.com/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/
Merge Two Sorted Lists - LeetCode
Level up your coding skills and quickly land a job. This is the best place to expand your knowledge and get prepared for your next interview.
leetcode.com
문제)
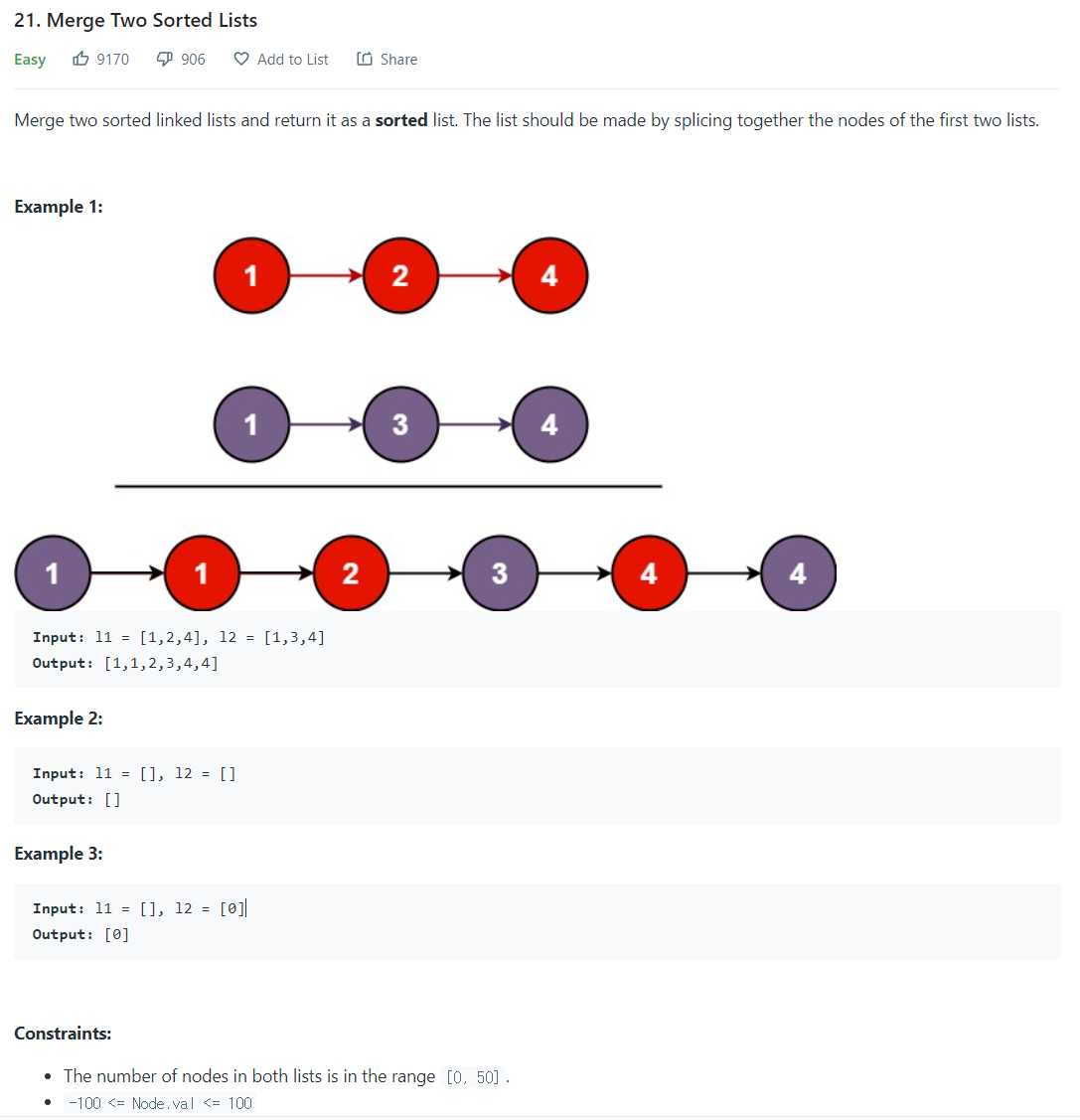
솔루션1) - iterative
l1 리스트를 기준으로 l2 리스트의 노드를 l1에 끼워놓는 방식입니다.
l2 노드가 l1에 insert가 될 때 이전 l1 노드의 주소를 알고 있어야 하므로 prev_l1 노드 정보를 계속 들고다녀야 합니다.
dummy 노드를 l1 노드 head에 연결하는 이유는 간결한 코드를 위해서 추가하였습니다.
dummy 노드의 최소값은 Node.val의 최소값이 -100 이브로 -100보다 작은 -200을 초기값으로 설정하였습니다.
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def mergeTwoLists(self, l1: Optional[ListNode], l2: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if l1 is None:
return l2
if l2 is None:
return l1
if l1 is None and l2 is None:
return None
dummy = ListNode(-200)
dummy.next = l1
prev_l1 = dummy
while l1 and l2:
if l2.val < l1.val:
temp = prev_l1.next
prev_l1.next = l2
next_l2 = l2.next
l2.next = temp
prev_l1 = l2
l2 = next_l2
else:
prev_l1 = l1
l1 = l1.next
if l1 is None:
prev_l1.next = l2
return dummy.next솔루션2) - iterative 간결
솔루션1)을 조금 더 간결하게 수정한 버전입니다.
tail 노드를 유지하면서 계속해서 tail에 노드를 추가해 가능 방식입니다.
코드가 훨씬 간결해지네요. 이해도 쉽습니다.
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def mergeTwoLists(self, l1: Optional[ListNode], l2: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
dummy = ListNode()
tail = dummy
while l1 and l2:
if l1.val < l2.val:
tail.next = l1
l1 = l1.next
else:
tail.next = l2
l2 = l2.next
tail = tail.next
if l1:
tail.next = l1
if l2:
tail.next = l2
return dummy.next
함께보면 좋은 영상:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XIdigk956u0
반응형
'알고리즘 > LeetCode' 카테고리의 다른 글
| LeetCode 풀기 - 1436. Destination City (0) | 2021.11.21 |
|---|---|
| LeetCode 풀기 - 1295. Find Numbers with Even Number of Digits (0) | 2021.11.21 |
| LeetCode 풀기 - 102. Binary Tree Level Order Traversal (0) | 2021.11.20 |
| LeetCode 풀기 - 733. Flood Fill (0) | 2021.11.17 |
| LeetCode 풀기 - 567. Permutation in String (0) | 2021.11.16 |
Comments




