| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
- 코틀린기초
- 릿코드풀기
- 파이썬릿코드
- python Leetcode
- 알고리즘풀이
- 파이썬알고리즘
- 파이썬 알고리즘
- 릿코드
- python priority queue
- 릿코드풀이
- 잇츠디모
- leetcode풀기
- 알고리즘풀기
- 파이썬릿코드풀기
- 파이썬 릿코드
- leetcode풀이
- 파이썬 프로그래머스
- python 알고리즘
- 릿코드 풀기
- 릿코드 파이썬
- python zip_longest
- python xor
- python 릿코드
- python sorted
- LeetCode
- binary search
- leetcode 풀기
- 파이썬 알고리즘 풀기
- 파이썬알고리즘풀기
- 상가수익률계산기
- Today
- Total
소프트웨어에 대한 모든 것
1962. Remove Stones to Minimize the Total 본문
문제)
1962. Remove Stones to Minimize the Total
You are given a 0-indexed integer array piles, where piles[i] represents the number of stones in the ith pile, and an integer k. You should apply the following operation exactly k times:
- Choose any piles[i] and remove floor(piles[i] / 2) stones from it.
Notice that you can apply the operation on the same pile more than once.
Return the minimum possible total number of stones remaining after applying the k operations.
floor(x) is the greatest integer that is smaller than or equal to x (i.e., rounds x down).
Example 1:
Input: piles = [5,4,9], k = 2
Output: 12
Explanation: Steps of a possible scenario are:
- Apply the operation on pile 2. The resulting piles are [5,4,5].
- Apply the operation on pile 0. The resulting piles are [3,4,5].
The total number of stones in [3,4,5] is 12.
Example 2:
Input: piles = [4,3,6,7], k = 3
Output: 12
Explanation: Steps of a possible scenario are:
- Apply the operation on pile 2. The resulting piles are [4,3,3,7].
- Apply the operation on pile 3. The resulting piles are [4,3,3,4].
- Apply the operation on pile 0. The resulting piles are [2,3,3,4].
The total number of stones in [2,3,3,4] is 12.
Constraints:
- 1 <= piles.length <= 105
- 1 <= piles[i] <= 104
- 1 <= k <= 105
솔루션1)
- 우선순위큐를 사용해서 문제 해결
- 우선순위큐를 put() 할 때 -를 취하고 get()할 때 -를 취해서 최대값을 얻게됨
- 최대값을 얻은 다음 division 2를 취하고 다시 우선순위 큐에 넣음
from queue import PriorityQueue
class Solution:
def minStoneSum(self, piles: List[int], k: int) -> int:
pq = PriorityQueue()
for n in piles:
pq.put(-n)
for i in range(k):
n = -pq.get()
n = math.ceil(n/2)
pq.put(-n)
ret = []
while pq.qsize():
ret.append(-pq.get())
return sum(ret)
결과가 너무 느리다!!

솔루션2)
- 솔루션1의 우선순위 PriorityQueue 사용을 heapq 자료구조 사용으로 변경함
- PriorityQueue는 내부적으로 heapq를 사용하며 thread-safe 코드로 인하여 heapq보다 속도가 느림
- heapq 사용으로 속도가 훨씬 빨라짐
- 알고리즘 문제 풀 때는 멀티 thread를 고려할 필요가 없기 때문에 locking 오버헤드가 없는 heapq를 사용하자!
import heapq
class Solution:
def minStoneSum(self, piles: List[int], k: int) -> int:
heap = [-n for n in piles]
heapq.heapify(heap)
for _ in range(k):
n = -heapq.heappop(heap)
n = math.ceil(n/2)
heapq.heappush(heap, -n)
return -sum(heap)
PriorityQueue vs heapq
Queue.PriorityQueue is a thread-safe class, while the heapq module makes no thread-safety guarantees.
The heapq module offers no locking, and operates on standard list objects, which are not meant to be thread-safe.
This makes the heapq module faster; there is no locking overhead. In addition, you are free to use the various heapq functions in different, novel ways, the PriorityQueue only offers the straight-up queueing functionality
출처 : https://stackoverflow.com/questions/36991716/whats-the-difference-between-heapq-and-priorityqueue-in-python
솔루션3)
- 솔루션2의 heappop(), heappush() 대신에 이를 더 효율적으로 수행하는 heaprelace()를 사용
import heapq
class Solution:
def minStoneSum(self, piles: List[int], k: int) -> int:
heap = [-n for n in piles]
heapq.heapify(heap)
for _ in range(k):
n = -heapq.heappop(heap)
n = math.ceil(n/2)
heapq.heappush(heap, -n)
return -sum(heap)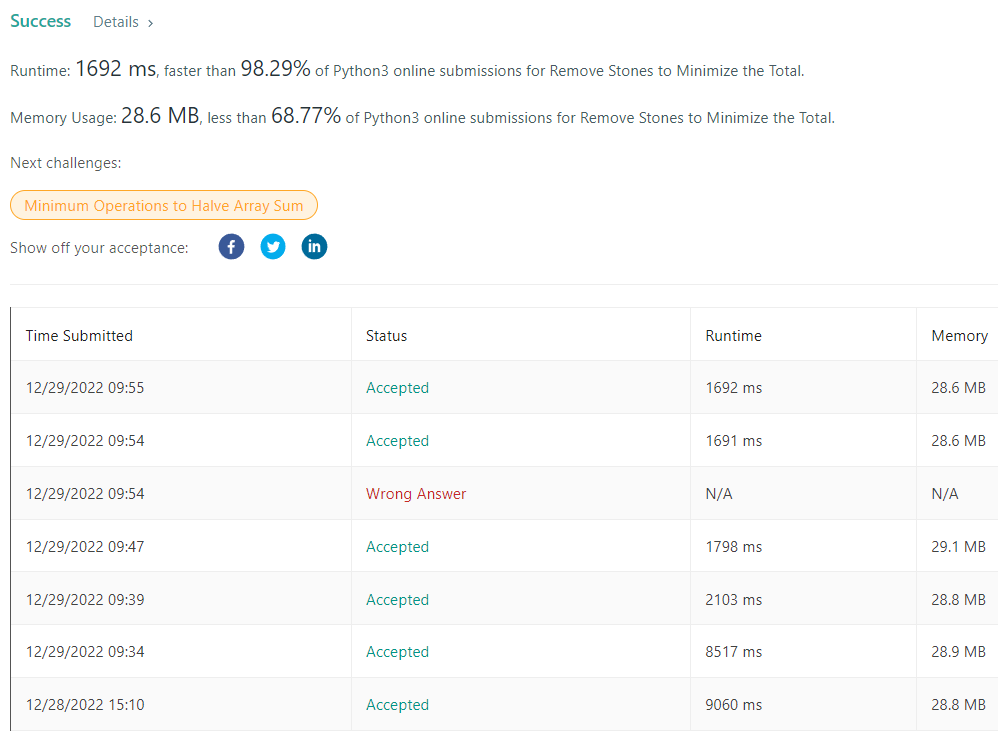
heapq.heapreplace(heap, item)
heap에서 가장 작은 항목을 팝하고 반환하며, 새로운 item도 푸시합니다. 힙 크기는 변경되지 않습니다. 힙이 비어 있으면, IndexError가 발생합니다.
이 한 단계 연산은 heappop()한 다음 heappush()하는 것보다 더 효율적이며 고정 크기 힙을 사용할 때 더 적합 할 수 있습니다. 팝/푸시 조합은 항상 힙에서 요소를 반환하고 그것을 item으로 대체합니다.
반환된 값은 추가된 item보다 클 수 있습니다. 그것이 바람직하지 않다면, 대신 heappushpop() 사용을 고려하십시오. 푸시/팝 조합은 두 값 중 작은 값을 반환하여, 힙에 큰 값을 남겨 둡니다.
출처 :https://docs.python.org/ko/3/library/heapq.html
'알고리즘 > LeetCode' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 290. Word Pattern (0) | 2023.01.01 |
|---|---|
| 1534. Count Good Triplets (0) | 2022.12.29 |
| 404. Sum of Left Leaves (0) | 2022.12.28 |
| 872. Leaf-Similar Trees (0) | 2022.12.27 |
| 2149. Rearrange Array Elements by Sign (0) | 2022.12.27 |




